Digital Twins in Manufacturing: Revolutionizing the Future of Production
- Madeline Medensky
- March 10, 2025
In the evolving landscape of advanced manufacturing, digital twin technology has emerged as a transformative tool, reshaping how industries design, operate, and optimize production processes. As companies navigate the challenges of globalization, rising customer demands, and increasing competition, integrating digital twins into their operations has become essential for achieving efficiency, sustainability, and innovation.
This blog delves into the profound impact of digital twins in manufacturing, exploring their applications, benefits, and the future they promise for the industry.

Digital twins can be used to bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds.
What is a Digital Twin in Manufacturing?
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, system, or process. In manufacturing, digital twins serve as dynamic, real-time models that mirror the behavior and state of real-world assets or processes. These digital models are powered by advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), which continuously collect and analyze real-time data from their physical counterparts.
Unlike static models or traditional simulations, digital twins are dynamic, enabling manufacturers to monitor, predict, and optimize their operations with unprecedented precision. They bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds, offering actionable insights that lead to informed decisions and transformative outcomes.
One area of precise application is in the laser scanning and reality capture industry, where industries, particularly manufacturing plants and facilities, rely on laser scan data to create versatile digital twins that visualize key manufacturing processes and equipment.
How Digital Twin Technologies Optimize Production
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
By leveraging IoT sensors embedded in physical assets, digital twins enable real-time data collection on machinery performance, temperature, vibration, and other key parameters. This data allows manufacturers to anticipate equipment failures, schedule predictive maintenance, and reduce unplanned downtime.
For instance, a digital twin of a factory robot can analyze usage patterns and predict when a component is likely to fail, ensuring timely repairs and uninterrupted operations.
2. Process Optimization
Digital twins provide manufacturers with a virtual environment to simulate and analyze different production scenarios. By tweaking parameters in the digital model, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and improve efficiency without disrupting the actual manufacturing process.
Simulate asset tagging in a virtual environment to instantly understand the site conditions.
This iterative optimization leads to reduced waste, faster production cycles, and lower operational costs.
3. Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
Supply chains are critical to manufacturing success, yet they remain vulnerable to disruptions. Digital twins enable manufacturers to model their supply chain networks, simulate potential disruptions, and test mitigation strategies. By integrating real-time data from suppliers, logistics, and inventory systems, digital twins help manufacturers maintain agility and continuity in their supply chains.
Key Applications of Digital Twins in Manufacturing
1. Product Design and Development
Digital twins are invaluable during the design phase of a product's lifecycle. Engineers can create virtual prototypes to test various designs, materials, and manufacturing techniques before committing to physical production. This approach reduces time-to-market and enhances product quality by identifying potential flaws early in the development process.
2. Smart Factory Optimization
Advanced manufacturing facilities increasingly rely on digital twin technologies to achieve "smart factory" status. By integrating digital twins with IoT, AI, and ML, manufacturers can monitor production lines in real-time, optimize energy usage, and maximize throughput.
For example, a digital twin of an entire production process can simulate the impact of adjusting machine speeds or changing material inputs, enabling faster and more efficient decision-making.

Digital twins can help teams visually understand their site and site conditions, enabling them to tag assets and segment pipeline to make smarter decisions about factory overhauls.
Sometimes, this is also referred to as transitioning to a virtual factory approach, where the analyses and operations can be run virtually around the as-built or as-installed space, giving power back to engineers, builders, managers and coordinators with how they implement or overhaul new design layouts or update equipment and machinery.
3. Worker Training and Safety
Digital twins create immersive virtual environments that simulate real-world manufacturing conditions. These simulations are used to train workers, teach safety protocols, and test emergency scenarios. By providing a risk-free training platform, digital twins enhance worker preparedness and reduce workplace accidents.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
As sustainability becomes a top priority for manufacturers, digital twins play a crucial role in minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and improving resource efficiency. They enable manufacturers to track and optimize energy use, assess the environmental impact of production processes, and design eco-friendly products. By transitioning to digital twin environments, it also reduces the impact of travel and potential worker safety hazards, scaling back on in-person site visits altogether. Learn how one company transformed their facility and maintenance programs to opt in for more sustainable and safe principles using Cintoo.

The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Digital Twins
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are the engines that power digital twins, enabling them to process vast amounts of real-time data and derive actionable insights. These technologies allow digital twins to:
Predict Future Outcomes: By analyzing historical and real-time data, digital twins can forecast production trends, equipment failures, and supply chain disruptions.
Enable Autonomous Decision-Making: Machine learning algorithms enable digital twins to recommend or execute actions without human intervention, such as adjusting machine settings to optimize performance.
Continuously Improve: Digital twins learn from new data, becoming smarter and more accurate over time. This self-improvement ensures that manufacturers stay ahead in an ever-changing market.
Integrating Digital Twins into the Real World
For manufacturers to unlock the full potential of digital twin applications, seamless integration with existing systems and processes is essential. For those projects in construction, renovation, maintenance, or facility updates, you’ll want a digital twin that mirrors real-world conditions so you can collaborate in the environment at any time, no matter where your team is located in the world either.
For full benefits, digital twins must integrate seamlessly with current systems. They should mirror real conditions for construction, renovation, or maintenance projects. This lets teams collaborate anytime, anywhere in the world.
Cintoo allows you to upload unlimited scan data to create a seamless navigational and visualization experience. Using a mesh-based engine, Cintoo’s ability to stream 3D scan data in high-quality meshes means there’s no compromise to accuracy, allowing your teams to work in an environment that allows you to build out a digital twin with autonomous programs.
Part of the beauty lies in the type of web-based, easily configurable application that Cintoo is. Cintoo works with any scan data, including 3D models from BIM/CAD programs, so you can measure and annotate on demand, align models with real-world conditions, and detect clashes or errors seamlessly.
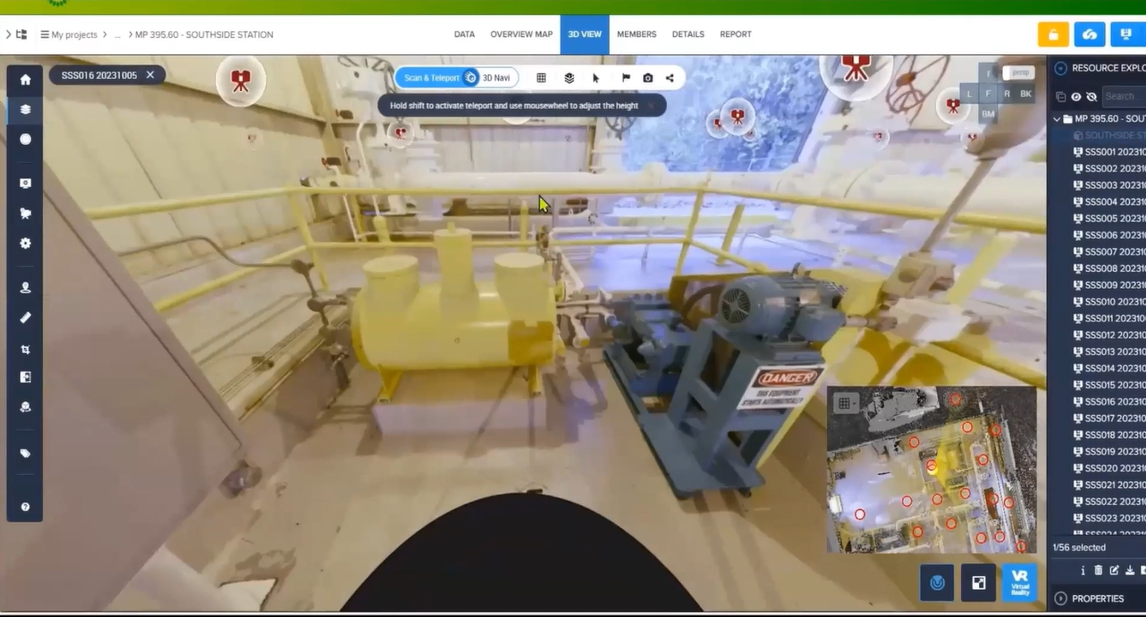
Tools like Cintoo’s comparison tool allows you to toggle between views of the as-built conditions on their own or with the modelled equipment in place. Getting up close and personal is no problem due to Teleportation, another tool that allows you to jump to any position in your scan data.
Cintoo’s comparison tool in action–comparing as-built and modelled conditions.
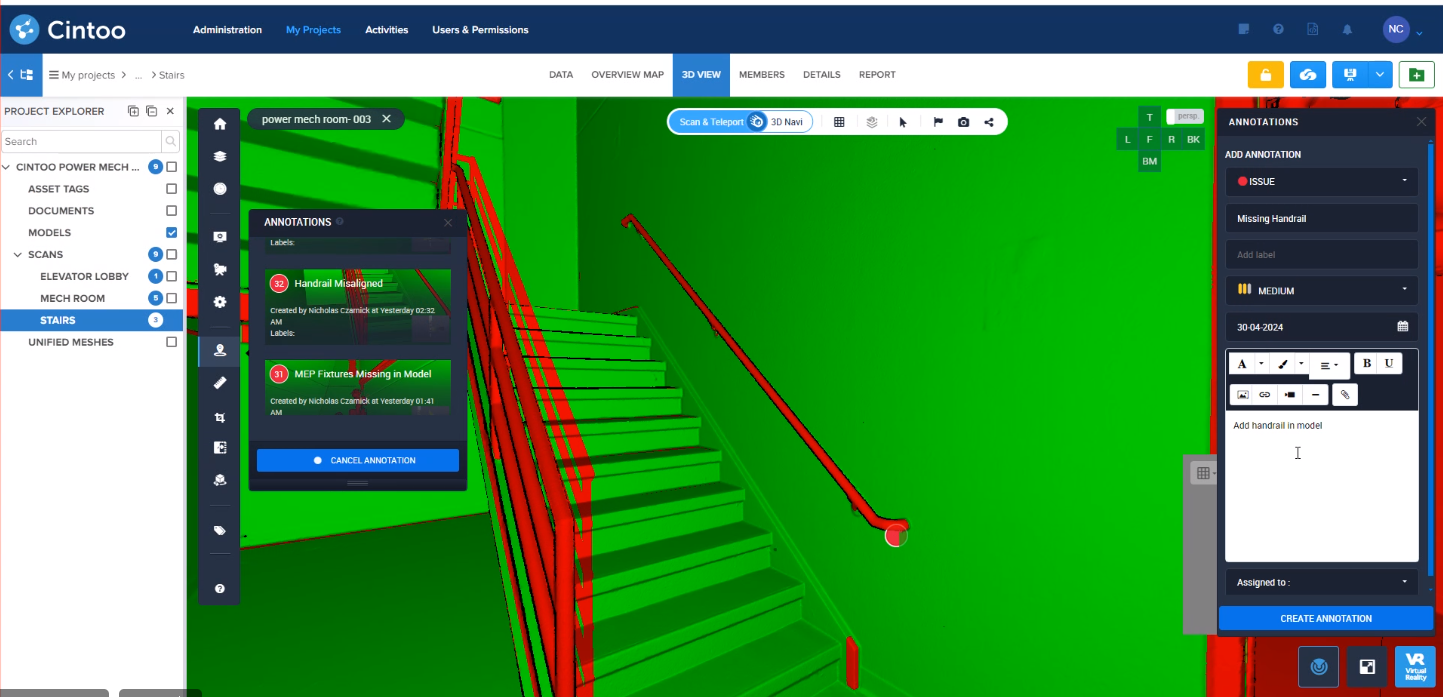
AI classification is also central to having digital twins for manufacturing. With AI engines built into product offerings, you can do more with your data. For instance, classify equipment at the touch of a button in Cintoo, including safety equipment, pipelines, and even whole segmentations of pipelines throughout a site.
AI classification is crucial for manufacturing digital twins. Built-in AI lets you do more with data. For example, classify equipment quickly in Cintoo, like safety gear and pipelines. This includes segmenting entire pipelines across a site.
All of this points to the fact that digital twins in manufacturing become inherently useful for simulating real-world conditions, which means other tools help draw more power from the data and collaborate across it.
Challenges and Opportunities
While digital twins offer immense benefits, their adoption is not without challenges. High initial investment costs, data integration complexities, and cybersecurity concerns are common hurdles. However, these challenges are outweighed by the long-term advantages of increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced innovation.
The rise of digital twins represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing, enabling businesses to move beyond reactive decision-making and embrace a proactive, data-driven approach. By creating virtual replicas of physical assets, manufacturers can monitor their operations in real-time, simulate potential scenarios, and make informed decisions that optimize production processes and strengthen the supply chain.
Digital twins mark a paradigm shift in manufacturing. They help businesses move from reactive to proactive, data-driven decisions. Virtual replicas of physical assets allow real-time monitoring. Manufacturers can simulate scenarios and make informed decisions. These optimize production and strengthen the supply chain.
In the end, the digital twins ultimately enable manufacturers to bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds, ensuring that every aspect of the production process is as efficient, reliable, and innovative as possible. This powerful technology is not just a tool for optimization—it's a cornerstone of the future of manufacturing.
For more insights, download our comprehensive e-book on digital twins in manufacturing.
.png?width=1080&height=500&name=CTA%20e-book%20Digital%20Twin%20-%20blog%20Cintoo%20(1).png)